Class 12 biology chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy flow solutions
Maharashtra Biology Textbook Solutions for Class 12 are very important and crusial that helps the students in understanding the complex topics and helps them in the preparation of class 12 board examination as well as verious compititive entrance examinations also. Studying the answers to the questions in the biology textbook will check your understanding of a particular topic and helps you determine your strengths and weaknesses.
Class 12 biology textbook Solutions for Class 12, Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy flow maharashtra state board are provided here with simple step-by-step detailed explanations. These solutions for Ecosystems and Energy flow are very popular among Class 12 students for biology chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy flow Solutions come handy for quickly completing your homework and preparing for exams. All questions and answers from the biology textbook Solutions Book of Class 12 biology Chapter 14 are provided here for you for free. You will also love the experience on ybstudy class 12 Solutions. All biology textbook Solutions. Solutions for class 12, These biology textbook solutions are prepared by biology experts and are 100% accurate.
Q. 1 Multiple choice questions
1. Which one of the following has the
largest population in a food chain?
a. Producers
b. Primary consumers
c. Secondary consumers
d. Decomposers
2. The second trophic level in a lake is
________________
a. Phytoplankton
b. Zooplankton
c. Benthos
d. Fishes
3. Secondary consumers are __________
a. Herbivores
b. Producers
c. Carnivores
d. Autotrophs
4. What is the % of photosynthetically
active radiation in the incident solar
radiation?
a. 100%
b. 50 %
c. 1-5%
d. 2-10%
5. Give the term used to express a community in its final stage of succession?
a. End community
b. Final community
c. Climax community
d. Dark community
6. After landslide which of the following
type of succession occurs?
a. Primary
b. Secondary
c. Tertiary
d. Climax
7. Which of the following is most often
a limiting factor of the primary
productivity in any ecosystem.
a. Carbon
b. Nitrogen
c. Phosphorus
d. Sulphur
Q. 2 Very short answer question.
1. Give an example of ecosystem which
shows inverted pyramid of numbers.
Answer : Pyramid of number indicates the number of individuals at each trophic level. The pyramid of number is inverted in tree ecosystem. In this, the the first trophic level contains least number of trees.
2. Give an example of ecosystem which
shows inverted pyramid of biomass.
Answer : There are two main types of biomass pyramid – inverted pyramid of biomass and the upright one. A good example of the inverted pyramid is in a pond ecosystem where the mass of phytoplankton, the major producers, will always be lower than the mass of the heterotrophs like fish and insects.
3. Which mineral acts as limiting factor for productivity in an aquatic ecosystem.
Answer : Phosphorus is a limiting nutrient in many terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. The productivity of the primary producers in these areas is limited, held in check, by the amount of available phosphorus that is so vital for life.
4. Name the reservoir and sink of carbon in carbon cycle.
Answer : Carbon is the chemical backbone of all life on Earth. Most carbon is stored in rocks and sediments, while the rest is stored in the ocean, atmosphere, and living organisms. These are the reservoirs, or sinks, through which carbon cycles. The ocean is a giant carbon sink that absorbs carbon.
Q. 3 Short answer questions.
1. Distinguish between upright and
inverted pyramid of biomass
Answer : Upright pyramid
1. Producers are more in numbers than the herbivores and herbivores more in number than carnivores.
2. Pyramid of energy is always upright.
3. Energy at lower trophic level is more than that in the higher level.
Inverted pyramid
1. Pyramid of biomass in a sea is inverted as the biomass of consumers (Fish) is more than that of producers (phytoplanktons).
2. Energy at lower trophic level is lesser than that of higher level.
2. Distinguish between Food chain and
Food web.
Answer :
- A food web consists of many food chains. A food chain only follows just one path as animals find food.
- eg: A hawk eats a snake, which has eaten a frog, which has eaten a grasshopper, which has eaten grass.
- A food web shows the many different paths plants and animals are connected.
- eg: A hawk might also eat a mouse, a squirrel, a frog or some other animal. The snake may eat a beetle, a caterpillar, or some other animal. And so on for all the other animals in the food chain.
- A food web is several food chains connected together.
Q 4. Long answer questions.
1. Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
Answer : Ecological pyramid is a graphic
representation of the relationship between the organisms of various successive trophic levels with respect to energy, biomass and number.
A pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation of biomass present in a unit area of various trophic levels. It shows the relationship between biomass and trophic level quantifying the biomass available in each trophic level of an energy community at a given time.
A pyramid of numbers is a graphical representation that shows the number of organisms at each trophic level. It is an upright pyramid in light of the fact that in an ecosystem, the producers are always more in number than other trophic levels. The pyramid of numbers was advanced by Charles Elton in 1927.
2. What is primary productivity? Give
brief description of factors that affect
primary productivity.
Answer : Productivity refers to the rate of
generation of biomass in an ecosystem. It is
expressed in units of mass per unit surface (or volume) per unit time, for instance grams per square metre per day (g/ m2/ day). The mass unit may relate to dry matter or to the mass of carbon generated.
It can be divided into gross primary
productivity (GPP) and net primary productivity (NPP). Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. Plants themselves use a considerable proportion of this GPP for their respiration. Hence, gross primary productivity minus respiratory losses
(R) constitute the net primary productivity
(NPP).
Net primary productivity is the
available biomass for the consumption, to
heterotrophs (herbivores, carnivores and
decomposers). The annual net primary
productivity of the whole biosphere is
approximately 170 billion tons (dry weight) of organic matter. Of this, the productivity of the oceans is only 55 billion tons.
Primary productivity (GPP) depends on the
plant species inhabiting a particular area. It also depends on a variety of environmental factors, availability of nutrients and photosynthetic capacity of plants. Therefore, it varies in different types of ecosystems.
3. Define decomposition and describe
the processes and products of
decomposition.
Answer :
Decomposers break down complex organic matter into inorganic substances like carbon dioxide, water and nutrients, and the process is called decomposition.
The important steps in the
process of decomposition are fragmentation, leaching, catabolism, humification and mineralization.
Detritivores (e.g. earthworm) break down
detritus into smaller fragments or particles. This process is called fragmentation.
By the process of leaching, water soluble
inorganic nutrients go down (percolate) into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts. Bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus into simpler inorganic substances. This process is called as catabolism. It is important to note that all the above steps in decomposition operate simultaneously on the detritus.
Humification and mineralization occur
during decomposition in the soil. Humification leads to accumulation of partially decomposed, a dark coloured, amorphous, colloidal organic
substance called humus that is resistant to
microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate. Humus formation changes soil texture and increases water holding capacity of soil.
Being colloidal in nature humus serves as
a reservoir of nutrients. The humus is further degraded by some microbes and release of inorganic nutrients occurs by the process known as mineralisation.
Decomposition as a process requires
oxygen. Temperature and soil moisture are
the most important factors that regulate
decomposition indirectly to help soil microbes. Warm and moist environment favours decomposition whereas low temperature and anaerobic conditions inhibit decomposition.
4. Write important features of a
sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem.
Answer : Sedimentary cycles have their reservoirs in the Earth’s crust or rocks. Nutrient elements are found in the sediments of the Earth. Elements such as sulphur, phosphorus, potassium, and calcium have sedimentary cycles.
Sedimentary cycles are very slow. They take a long time to complete their circulation and are considered as less perfect cycles. This is because during recycling, nutrient elements may get locked in the reservoir pool, thereby taking a very long time to come out and continue circulation. Thus, it usually goes out of circulation for a long time.
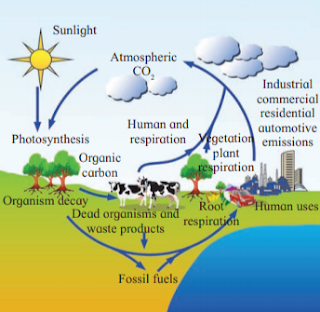
5. Discribe carbon cycle and add a note
on the impact of human activities on
carbon cycle.
Answer :
The carbon cycle is the process in which carbon travels from the atmosphere into organisms and the Earth and then back into the atmosphere. Plants take carbon dioxide from the air and use it to make food. Animals then eat the food and carbon is stored in their bodies or released as CO2 through respiration.
All life forms on earth are carbon based
because carbon is the main component of
all the organic compounds of protoplasm. It constitutes 49% of dry weight of organisms. If we look at the total quantity of global carbon, we find that 71% carbon is found dissolved in oceans. This oceanic reservoir regulates the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Human activities have a tremendous impact on the carbon cycle. Burning fossil fuels, changing land use, and using limestone to make concrete all transfer significant quantities of carbon into the atmosphere. The ocean absorbs much of the carbon dioxide that is released from burning fossil fuels.